How Third-Party Auditors Make Oil Industry Fraud Possible
The accounting companies hired by oil companies to evaluate their inflated financial claims are on the hook from investors frustrated by the lack of accountability.

Major accounting firm KPMG is under fire from investors who filed a class action lawsuit against the firm for overstating the asset values of now-defunct oil exploration company Miller Energy Resources. And last month, a judge dismissed KPMG’s attempt to have the case thrown out.
At issue in the lawsuit, filed in 2016, is a $4.55 million purchase by Miller Energy in 2009 for land and offshore oil assets in Alaska which included existing oil production infrastructure. Miller Energy then claimed those same assets were worth approximately half a billion dollars, a claim which would require approval by third-party auditors.
But according to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the property and old oil infrastructure in Alaska was worth only a fraction of those claims; inflating its value beyond its worth amounted to fraud, according to the SEC. The SEC stated that “Miller Energy overvalued the Alaska assets by more than $400 million.” But the oil company wasn’t the only one at fault, said the SEC. In January 2016, the SEC sent a cease and desist order for Miller Energy detailing the major fraud case and focusing in part on the role that third-party auditors such as KPMG played in making it possible.
The onshore and offshore Alaskan oil assets purchased by Miller Energy had been abandoned by the previous owner because the asset retirement obligations (AROs) — the amount of money required to properly decommission the existing assets — were likely greater than the value of the remaining oil in the ground. The property was essentially worthless once the cost of the AROs was considered. But Miller Energy then told the SEC in 2010 that property was worth half a billion dollars and KPMG signed off on that estimate for several years, starting in 2011.
In an August 2017 cease and desist order for KPMG, the SEC summarized the extent of KPMG’s failure to perform a valid audit of Miller Energy:
“[T]he KPMG engagement team performed an inadequate assessment of the risks associated with the Miller Energy engagement. Among other things, KPMG’s initial evaluation, which was completed by Riordan and approved by KPMG management, failed to adequately consider Miller Energy’s bargain purchase, its recent history as a penny-stock company, its lack of experienced executives and qualified accounting staff, its existing material weaknesses in internal control over financial reporting, its long history of reported financial losses, and its pressing need to obtain financing to operate the newly acquired Alaska Assets.”
The Miller Energy executive who signed off on the overvaluation ultimately paid an SEC fine of $125,000, while KPMG was fined $1 million.
Oil reserves fraud — in which companies overestimate the amount of oil that can be produced from their assets — has been recognized as a growing problem in the oil and gas industry, as DeSmog has previously reported. But in order for companies to succeed in convincing investors of their incredible claims, it is critical to have independent third-party auditors — like KPMG — to support these claims.
A Seal of Approval on Fraud
Having third-party professionals sign off on corporate financial reporting is a standard part of doing business. The idea is to have independent parties verify that the reports are accurate. When companies are engaged in fraud, getting an apparently reputable third party to put its name on the financial reporting is one way to hide the fraudulent dealings, while also offering plausible deniability to those committing the fraud.
Much like the role of Enron’s auditor, the major accounting firm Arthur Andersen, whose “audits were meant to, and did, act as a seal of approval, a willingness to put a stamp of good practice on Enron transactions,” as Slate described in 2002, Miller Energy found a third party to sign off on its questionable financials: the small firm Sherb & Co.
And just like that seal of approval by a supposedly independent auditor ended up being the downfall of Arthur Andersen — then part of The Big Five accounting firms in the U.S. — and saw Enron’s top executives go to prison, so too are Miller Energy and its auditors’ activities now under scrutiny.
Sherb & Co. completed audits for Miller Energy in 2009 and 2010. Then, in 2013, the SEC found “that Sherb & Co. LLP and its auditors falsely represented in audit reports that they had conducted the audits in accordance with U.S. auditing standards when in fact they were riddled with failures and improper professional conduct.”
But by that time Miller Energy had switched, in 2011, to a new auditing firm to validate the claim that the land and oil infrastructure the company purchased in Alaska was worth one hundred times what it paid for it: Big Fouraccounting firm KPMG.
SEC and Miller Energy
In August 2017, the SEC charged KPMG with “audit failures” in its work with Miller Energy.
“Auditing firms must fully comprehend the industries of their clients. KPMG retained a new client and failed to grasp how it valued oil and gas properties, resulting in investors being misinformed that properties purchased for less than $5 million were worth a half-billion dollars,” Walter E. Jospin, Director of the SEC’s Atlanta Regional Office, said in a statement at the time.
The SEC’s 2016 order against Miller Energy recounted the details of a 2010 call in which the management discussed how to validate the oil company’s inflated asset valuations. On that call, the Miller Energy CFO reportedly told the other participants that “a professional had to sign off on it, not us, some third party…”

Financial reporting at the heart of the matter in 2010 showed an increase in asset value of over $490 million for Miller Energy, compared to 2009 when the company had assets of less than $10 million. Essentially, the company’s entire value in 2010 was attributable to the Alaskan assets.
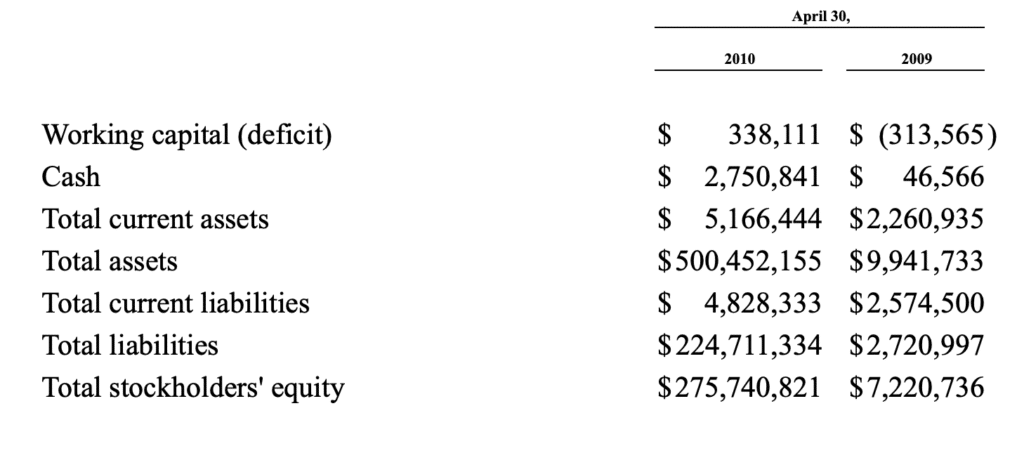
Both Sherb & Co, and later KPMG, audited and approved that valuation.
Then, in April 2011 the SEC sent a letter to Miller Energy with some questions about its annual 10-K filing from the previous year, first asking the oil company to explain its valuation of the Alaskan property.
Starting with its response to this question, Miller Energy went all-in on its fraudulent claims and shielded itself with the veneer of credibility from a Big Four accounting firm.
“The Management is Incompetent”
According to SEC documents, KPMG was retained as Miller Energy’s independent auditor on February 1, 2011. Two months later, on April 13, executives for the oil exploration firm rang the opening bell on the stock market floor as the company was listed on the New York Stock Exchange. It was a big moment for a company with no history of profits and that had been trading as a penny stock before the Alaska purchase.
That day, Miller Energy CEO Scott Boruff gave an interview on the trading floor, mentioning his company’s “explosive growth” and its bright future prospects. Boruff was paid $7.6 million in 2011.
Boruff was joined that day by company founder Delroy Miller, who also happened to be his father-in-law. While this arrangement apparently didn’t raise any questions with auditors, in 2014 their relationship was flagged in more SEC correspondence from “Concerned Miller Shareholders (CMS)”:
“In the absence of proper qualifications, CMS has raised reasonable questions surrounding Mr. Boruff’s appointment as Miller’s CEO and specifically, whether it was motivated by his close familial ties to the Company’s founder.”
Boruff had no oil industry experience before being appointed in 2008 as CEO by his father-in-law. However, Boruff did have experience with companies involved in financial fraud, as lawyers for CMS noted.
According to CMS correspondence with the SEC, in a section titled “The Management is Incompetent,” Boruff had previously worked at the firm GunnAllen Financial, leaving in October 2006, and that “GunnAllen has since been closed by regulators [in 2010] and entered bankruptcy in the wake of investor lawsuits and allegations of a major Ponzi scheme involving Provident Asset Management.”
Provident was a good old-fashioned Ponzi scheme, promising investors eye-popping 18 percent returns from oil and gas royalties. In reality, however, the company paid those returns with money coming from new investors. The scam involved almost a half-billion dollars.
But Boruff, who worked as a broker at GunnAllen, was not charged in that Ponzi scheme. Instead of distancing himself from it, however, as the new head of Miller Energy, he hired Darren Gibson in 2009, who according to documents sent to the SEC, “was Provident’s former National Sales Director during the alleged Ponzi scheme.”
Announcing the new hire in a press release, Boruff said “[Gibson]’s proven track record in raising capital will allow Miller to aggressively pursue our acquisition and drilling program goals.”
But Boruff and Gibson’s proven track record should have raised red flags to auditors evaluating the company’s financial records, especially given the pair’s lack of oil and gas industry experience.
Despite all this, KPMG continued rubber-stamping Miller’s financial statements even after the concerned shareholders had been communicating with the SEC.
Reserves Fraud and Asset Retirement Obligations
As DeSmog has reported, oil and gas companies inflating the values or volumes of their reserves estimates lies at the heart of much of the fraud now surfacing in the industry. Miller Energy is just one example of many.
Another major factor is how oil companies get around financial obligations to clean up their old wells and surrounding lands after they are done extracting oil and gas — known in the industry as asset retirement obligations (AROs). These obligations are increasingly becoming an issue as oil and gas companies try to sell old assets because the cleanup liabilities are likely greater than the value of the oil and gas. This was the case with Miller Energy.
The asset retirement obligations for the Alaskan property Miller acquired were the reason why no one else wanted to buy it.
In July 2010, the SEC asked questions about Miller’s AROs and noted that in 2009, “a third party report had indicated that the AROs for these assets were $41 million.”
Miller Energy’s finances were rife with red flags. Enough even to get one engineering firm, with prior experience with the Alaskan property Miller purchased, to walk away. According to the SEC, this was because the firm “refused to assign any value to a property known as the Redoubt Shoal field [a major part of the Alaskan assets Miller acquired, which was then valued at $291 million by Miller], because it was uneconomical … and the prior firm had explained that it would not put its ‘name on a report that implies value exists where it likely does not.’”
After its Alaska deal, Miller Energy not only needed an auditor to give its seal of approval to claims that its property and oil infrastructure in Alaska had some value, it would require an auditor to agree it was worth half a billion dollars. KPMG was willing to do this.
Third-Party Auditors and KPMG
In 2017, the SEC laid out the many failures of KPMG in the Miller Energy case, including that the evidence that something was wrong should have been obvious to anyone who knew to look for it: “All of these facts were readily ascertainable from the publicly available bankruptcy records of the prior owner of the Alaska Assets. If they had reviewed those records, KPMG would have learned that their understanding of the facts leading to the acquisition was inaccurate.”
The SEC also noted that, like the CEO of Miller Energy, the partner whom KPMG put in charge of the audit, John Riordan, lacked relevant oil and gas industry experience, “resulting in departures from professional standards.”
But the issue was not just one partner at KPMG, according to the SEC, which noted that company management and national personnel “became aware of the unusual and highly material prior-year transaction,” yet “the firm did not take sufficient action.”

As the SEC also noted in this case, due diligence requires an auditor to exercise professional skepticism — something the Miller valuation should have raised. Yet in 2011, when the financial website Street Sweeper published research challenging Miller Energy’s financial claims, KPMG chose to overlook those red flags as well, says the SEC. Now defunct, Street Sweeper was known for reporting on “over-valued, over-hyped stocks on Wall Street.”
The SEC noted that KPMG’s Department of Professional Practices (DPP), which was responsible for developing the firm’s internal auditing standards and guidance, failed to step in despite its knowledge of the Miller Energy case.
The SEC concluded that “DPP’s decision not to inquire further about the valuation of the Alaska Assets was unreasonable in light of the circumstances.” It also added that once KPMG learned of the 2011 Street Sweeper report, the department should have provided oversight of both Miller’s assessment and its own company procedures for the valuation.
In August 2017, the SEC found KPMG guilty of a long list of violations with regard to its audits of Miller Energy, including “lack of competence” and “highly unreasonable conduct.”
While not specifically implicated in the Miller Energy audit, David Middendorf, the former head of KPMG’s DPP where he was responsible for “audit quality and professional practice,” was sentenced to prison in 2019 for his part in trying to cover up KPMG’s dismal auditing results from 2013 and 2014.
After being misled about the oil company’s financial realities, many investors in Miller Energy lost their entire investments, which is why they are now suing KPMG.
Investors Lose, Fraudsters Walk Away
In the end, the SEC settled the charges against KPMG and John Riordan, its partner overseeing the case. KPMG agreed to give back the money it earned from working for Miller Energy, which was a little over $5 million when interest was included. Additionally, KPMG paid a civil penalty of $1 million while Riordan was fined $25,000. Riordan remained a partner at KPMG until he retired in 2020.
KPMG did not respond to a request for comment on whether anyone at KPMG was held accountable for their role in the Miller Energy audit.
Miller Energy was also fined $5 million, but due to its 2015 bankruptcy, it is not clear if that amount was ever paid in full during the three years it had to make the payments. In 2016, the company was reorganized into new entities controlled by Apollo Investment Corporation.
The SEC did not respond to a request for information on the status of that payment.
For their roles in the fraud, Miller’s CFO Paul Boyd and COO David Hall were both personally fined $125,000.
Scott Boruff, the CEO who oversaw all of the fraudulent activity, was not fined. After leaving Miller Energy in March 2016 when the bankruptcy was finalized, Boruff was sued by his father-in-law for failure to repay a $6 million personal loan.
Meanwhile, defrauded investors have turned to a lawsuit against KPMG to try to recoup their losses. That lawsuit is now expected to proceed next year.
Jeffrey Skilling, CEO of Enron, spent 14 years in jail for misleading investors. Arthur Andersen ceased to exist as one of the Big Five accounting firms due to its role in the Enron fraud. Meanwhile, Miller Energy executives and KPMG have essentially walked away with fines irrelevant to the scale of the fraud.
The oil company executives who oversaw the company during this fraud kept the money they were paid.
As this case and many others make clear, there is little incentive for oil industry executives to play by the rules when a company can engage in blatant fraud, get caught, and suffer almost no consequences. However, these frauds require the help of a third-party auditor willing to look the other way.
And while there are clearly auditors and engineering firms who will not put their “name on a report that implies value exists where it likely does not,” as the SEC wrote, there are plenty of others who will — including some of the biggest names in the business.
This article originally appeared on DeSmog.



Comments ()